Characteristics of SGO solid lubricant acting on the friction surface
SGO
view : 1546
Today, we will look at the characteristics of graphite material , a solid lubricating agent applied to embedded oilless bearings , acting on the friction surface.
First, the solid lubricant is compression-molded and sintered by mixing graphite, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) and other resins, which are well known as lubricating components. It performs friction in a different way than grease fluid lubrication, a lubricant commonly used in mechanical devices.
Fluid lubrication is the most ideal form of lubrication as an oil film is formed when oil of sufficient thickness is supplied to both friction surfaces for friction movement, and both friction surfaces are separated from each other and are not in direct contact . However, it is not suitable for oilless bearings in environments where regular lubrication is difficult, and it is common to use a small amount of fluid lubricant in solid lubricants.
|
division |
Solid lubrication |
Fluid lubrication |
|
Main ingredient |
Graphite, molybdenum, tungsten sulfide |
Coal-based mineral oil |
|
Temperature |
450 degrees (based on graphite) |
Choose the right lubricant for your temperature range |
|
Installation environment |
No separate equipment required |
Equipment such as oil tank and piping required |
|
circumstance |
Less generation of oil vapor, dust, etc. |
Occurs a lot of oil vapor, dust, etc. |
|
life span |
Semi-permanent (around 8-10 years) |
Periodic replacement (within 6~8 months) |

Graphite, which is most commonly used as a solid lubricant, has a layer structure , the most stable chemical structure in the atmosphere . Each layer is bonded by Van Der Waals Force , which has a relatively weak bonding force, so it is easily decomposed even under a small stress. In a humid environment, it is rather advantageous for lubrication
※Van Der Waals Force : The closer the distance between neutral molecules or atoms , the stronger the attraction. The source of this force is the electrostatic attraction acting between dipole-dipole, dipole-induced dipole, and induced dipole-induced dipole, and this force is collectively referred to as van der Waals force. The van der Waals power comes from the name of the Dutch scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals (1837-1923). Van der Waals force refers to an intermolecular force that acts between molecules , and is distinguished from an intramolecular force such as an ionic or covalent bond caused by the bonding of atoms . The various physical properties of organic compounds, polymer compounds, and molecular solids are due to van der Waals forces.
The way graphite lubricates on the friction surface can be explained as follows. First, the abrasion material is partially cut away by initial friction, promoting the abrasion of the solid lubricant. At this time, the grease applied initially and the fluid lubricant impregnated into the pores of the porous solid lubricant play a role of helping lubrication. Next, the abrasive material, graphite particles, and lubricant are mixed to fill the empty space inside the friction surface, which forms a thick film and is applied to the friction surface. From then on, it will lubricate for a long time while maintaining a stable coefficient of friction.

This can also be confirmed through graphs of friction coefficient and friction temperature by time of oilless bearings. The following are some of the data that tested SGO's oilless bearings at high surface pressure. The vertical axis of the graph means friction coefficient and friction temperature , respectively, and the horizontal axis is the number of test cycles , which is the same as time.
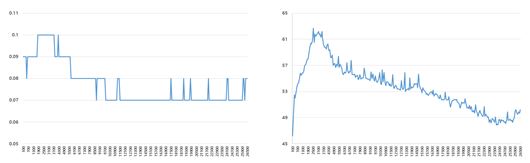
Both graphs increase in the initial friction stage, then gradually decrease, and then converge to a constant value. However , if a material or design that is not suitable for the surface pressure environment is applied, not only the shape of the graph is very unstable, but also the wear of the material itself is so severe that the problem of early replacement of the product may occur.
SGO has an infrastructure that can be designed and tested. We also have the technical capabilities to produce optimal products that meet various surface pressure conditions, so if you have any questions about oilless bearings, please feel free to contact us for technical research! :)