Various Casting Processes for Oilless Bearings
SGO
view : 1459
As industrial demands and applications increase, so does the demand for complex and high-quality products. Fortunately, there are many types of casting processes that can manufacture complex and precise products for a variety of applications and user needs.
It is helpful to understand the pros and cons of these methods in order to select the correct casting method for your manufacturing needs.
1. Casting Process Overview
The casting process is a manufacturing method in which molten metal is poured into a mold, hardened, and then cooled at room temperature to make a metal part of the desired shape. Complex parts can be produced regardless of size.
Casting can produce isotropic metal parts in large quantities and consequently is suitable for mass production. There are also different types of castings depending on the materials and molds used to meet specific user requirements.
2. Different types of casting process
There are different types of casting processes and each process has its own advantages and disadvantages depending on your requirements.
1) Sand casting process


- Sand Casting
Sand casting is a versatile casting process that can be used to cast ferrous or non-ferrous metal alloys. It is widely used in mass production of industrial units such as automotive metal casting parts such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, crankshafts, etc.
This process uses molds made of silica-based materials such as natural bonding or synthetic sand that form a smooth mold surface. There are two parts to the mold surface: corp (upper half) and drag (lower half). Using a pouring cup, molten metal is poured onto the pattern and allowed to solidify to achieve its final shape. Finally, the excess metal is trimmed to finish the final metal cast product.
2) Centrifugal Casting
Centrifugal casting is a process for industrially manufacturing cylindrical parts using centrifugal force. This type of metal casting uses a preheated rotating die into which molten metal is poured. Centrifugal force helps distribute molten metal within the die at high pressure.
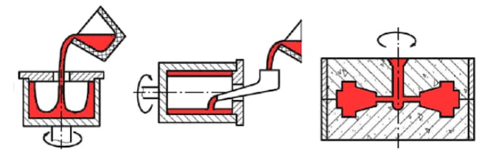
Centrifugal casting process
There are three variants of centrifugal casting. Full centrifugal casting process, semi-centrifugal casting process and vertical centrifugal casting process. Unlike true centrifugal casting, semi-centrifugal casting uses a sprue to completely fill the mold. However, in true centrifugal casting, molten metal sticks to the sides due to continuous rotation. In contrast, vertical centrifugal casting, as the name suggests, uses directional forming following the same process as true centrifugal casting.
In general, centrifugal casting produces rotational shapes such as cylinders. In particular, parts such as bush bearings, clutch plates, piston rings, and cylinder liners. In addition, by injecting metal into the center of the mold, it helps to reduce defects such as blowholes, shrinkage, and gas pockets. However, it is not suitable for all kinds of metal alloys.
4) Horizontal Continuous Casting
There are three types of continuous casting: horizontal, vertical downward, and vertical upward. In this letter, we will discuss horizontal continuous casting.
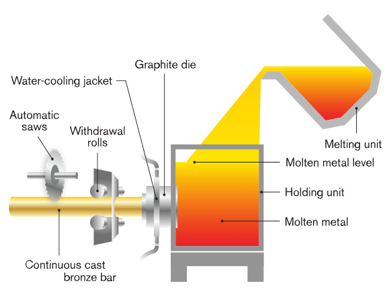
Production uses continuous casting, one of the most sophisticated methods of casting copper alloys. This metal casting method is most effective when large quantities of standardized semi-finished products are to be produced.
This method allows greater control over the process through automation.
Homogeneous semi-finished metal products can be obtained during the casting process through identical and continuous metal feed, crystallization and product removal, and enhanced cooling with water or distilled water can be used to speed up crystallization.
By selecting an appropriate speed, concentrated crystallization of the material (mainly in the casting length direction) can be achieved and a fine crystalline structure and chemical composition such as dense bar, semi-finished product can be produced.
A wide range of different profiles can be produced through continuous casting, which are listed below.
-List-
Cylindrical barrels (bar shape), tubes, square barrels, hexagonal bares, etc.
slabs of various thicknesses and widths, etc.